The beneath insightful new article penned by KuCoin’s founder, Michael Gan, and Head of Derivatives, Ken Tian, delves into the modern backend logic of KuCoin’s new threat restrict system for cross-margin, much like conventional finance, showcasing KuCoin’s dedication to technical excellence and strong threat administration methods.
Introduction
Many cryptocurrency exchanges undertake complicated threat administration measures to forestall liquidation dangers. These embody setting multi-level threat limits and proscribing the usage of excessive leverage. Moreover, exchanges dynamically regulate parameters like threat limits and margin charges primarily based on the underlying asset’s worth and market liquidity. Nevertheless, these processes will not be solely complicated but additionally lack clear administration requirements, requiring important sources to take care of a system that will not be internally constant—for instance, rising capital might not permit for bigger positions on account of abrupt modifications in leverage tiers.
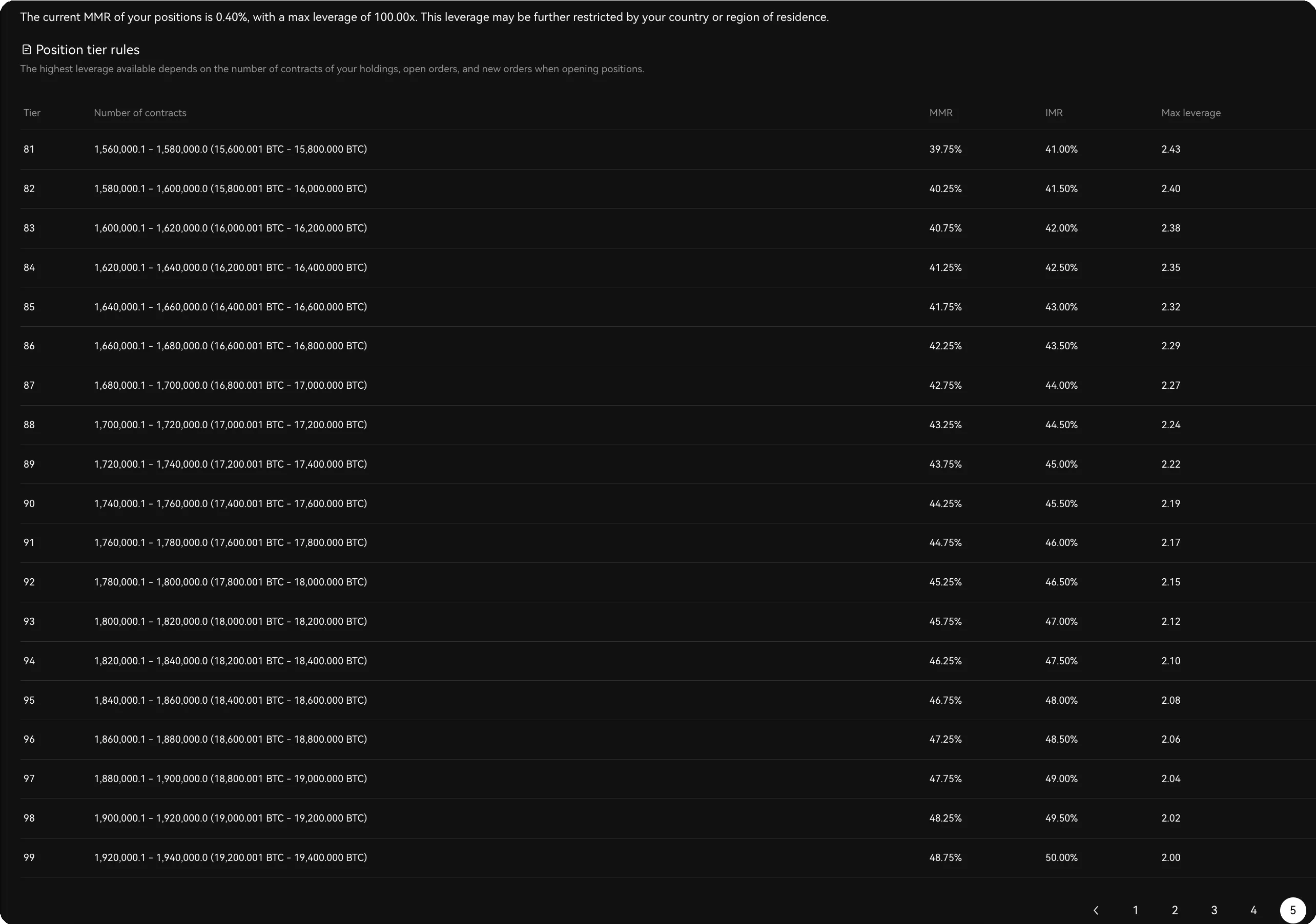
On some buying and selling platforms (see Determine 1), there are almost 100 threat restrict tiers. These passive tier modifications improve the complexity of system administration and may end up in partial compelled liquidation, undermining customers’ pursuits.
We purpose to develop a nonlinear mannequin to simulate cheap place sizes for a given capital, enabling extra versatile and environment friendly threat administration. This method entails rebuilding the inner system system to realize self-consistency, offering a viable various to the prevailing complicated threat restrict templates.
This paper proposes a brand new threat administration framework as a alternative for the present restrict fashions. The brand new method has already been carried out in KuCoin’s cross-margin system, exhibiting some apparent benefits:
- It’s nearer to the place administration settings utilized by conventional exchanges, making it simpler for institutional capital to adapt.
- It eliminates the necessity to regulate threat limits primarily based on place measurement or leverage utilization.
- It simplifies operational processes, decreasing the burden on the change whereas mitigating the chance of harming customers’ pursuits to guard the change’s personal advantages.
This mannequin gives a extra clear and streamlined method to threat administration, aligning each change operations and person pursuits.
The mannequin
Most Place Dimension
We assume {that a} person’s account holds capital C, and the worth of the underlying asset’s futures contract is p. The preliminary margin price r corresponds to the reciprocal of the leverage chosen by the person. Ignoring transaction charges, the variety of contracts the person can open is given by:
N = C/(p ∗ r)
Nevertheless, if the capital C is just too giant or the margin price r is just too low, the related dangers for the change develop into important. Subsequently, when each C and rrr are fastened and C is giant, the utmost allowable place can be restricted by the change’s threat tiers to a lot lower than C/(p*r). Conversely, with smaller capital C, the place measurement can method C/(p*r).
Many exchanges implement dozens to a whole lot of threat tiers to handle this relationship. Consequently, customers steadily want to regulate their tier degree as their capital grows. The target behind these restrictions might be roughly expressed utilizing a logarithmic perform:
N = ln(C/(p ∗ r) + 1)
Clearly, when C is giant, the primary spinoff of the logarithmic perform decreases, which means the achievable place measurement can be smaller than that calculated by a linear system. Nevertheless, this presents a problem: for the approximation ln(x+1)≈x to carry, C should be small enough, and p should be giant. In any other case, even with small C, customers should still be unable to realize the theoretical most place measurement of C/(p*r).
To handle this, we have to introduce a bigger scaling parameter ok primarily based on the traits of various contract varieties. The unique equation is then modified as follows:
N = ok ∗ ln(C/(p ∗ r ∗ ok) + 1)
This adjustment satisfies the wants of small-capital customers whereas additionally assembly the chance management necessities for large-capital customers.
To keep in mind open positions and different margin necessities in KuCoin’s cross-margin system, let’s outline the next:
- F: Margin occupied by different contracts and open orders.
- E: Complete fairness within the person’s futures account.
- Q: Place measurement of pending orders aligned with the identical route as the brand new order.
- O: Present open place measurement (optimistic if aligned with the brand new order, adverse if in the wrong way).
The equation for calculating the utmost allowable place is then:
N = max(0, ok ∗ ln((E − F )/(ok ∗ p ∗ r) + 1) − Q − O)
Subsequently, beneath this mannequin on KuCoin, for capital of a typical measurement, the connection between leverage and the utmost allowable place might be visualized as follows:
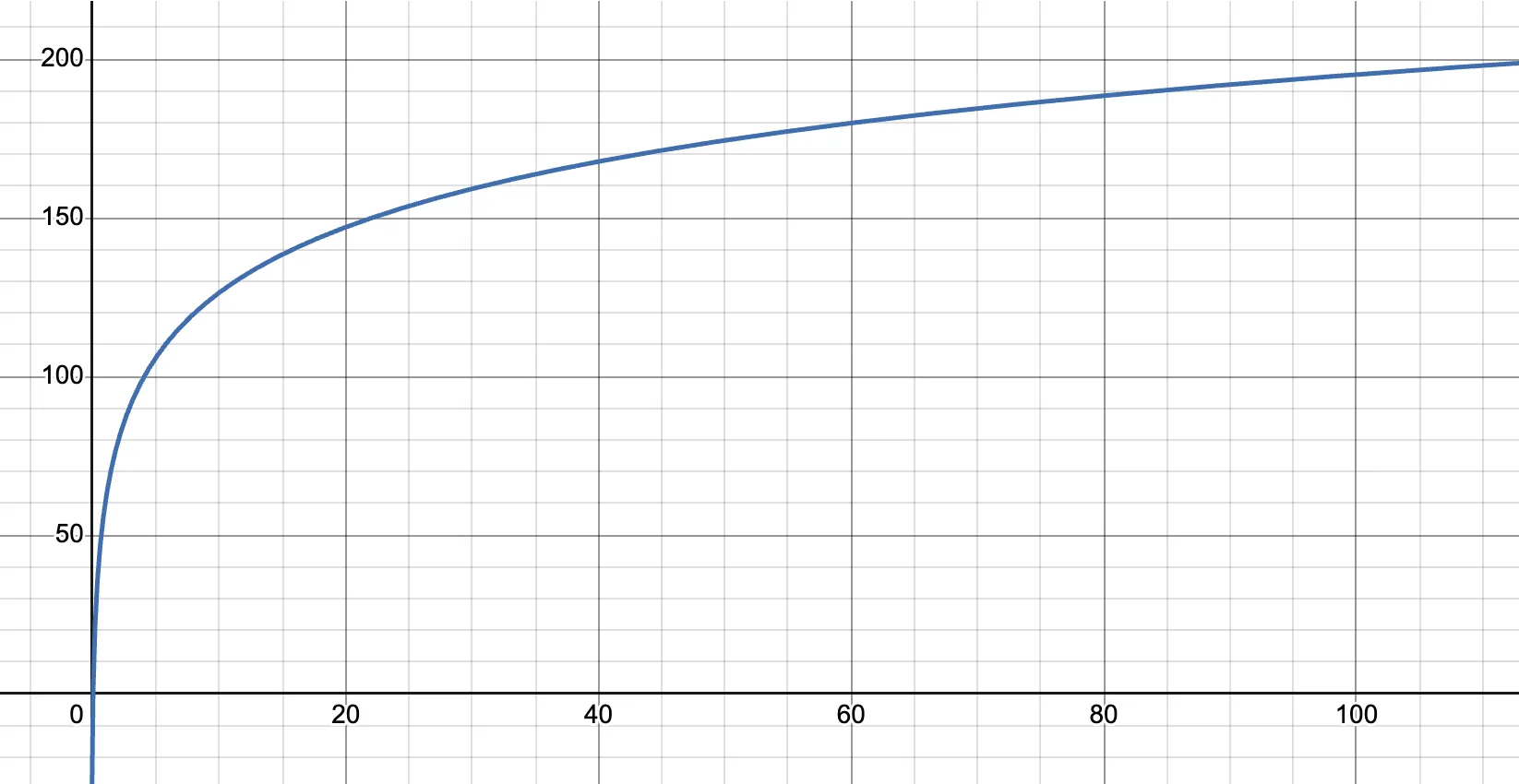
This chart displays how the mannequin ensures scalability and stability, balancing between the wants of smaller customers (to maximise place measurement) and threat management for bigger customers by way of nonlinear margin changes.
Nevertheless, on most exchanges (equivalent to OKX and Binance), the connection between leverage and place measurement typically follows a distorted curve:
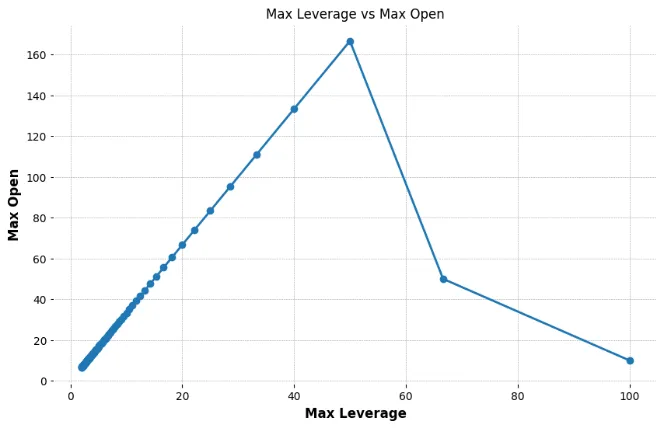
In truth, even MMR (Upkeep Margin Fee) follows an identical sample. This may be significantly difficult for large-capital customers. For instance, when the IMR (Preliminary Margin Fee) is ready at 50%, the MMR may be as excessive as 48%. In such instances, customers making an attempt to open giant positions are restricted to utilizing low leverage, however the MMR is elevated to an unreasonable extent.
This setup limits customers’ skill to successfully make the most of their capital, as leverage tiers shift abruptly and require frequent changes, decreasing flexibility. It creates an imbalance between threat administration and person expertise, making it tough for giant traders to function effectively inside these constraints.
MMR and IMR
The MMR (Upkeep Margin Fee) primarily serves as a compensation mechanism for the change to handle liquidation dangers. At its core, MMR displays the stress on liquidity extraction and wishes to regulate dynamically with modifications in open positions. Under, we derive the theoretical worth of MMR primarily based on liquidity-related metrics accessible to the change.
Liquidity-Associated Variables
To correctly assess liquidity, the next variables are recognized, that are sometimes accessible to exchanges:
- μ: Velocity of market order execution
- T: Time requirement for liquidation or buying and selling
- i: Value/degree distance from one of the best bid or askj: Ticker time unit
- Qi: Common variety of orders at a distance iii from the order e book
- S: Common measurement of an order (with SmS_mSm for market orders, SlS_lSl for restrict orders)
- N: Variety of orders (with Nm for market orders, Nc for cancellations, and Ni for restrict orders)
These values symbolize the typical circumstances in a secure market.
Defining Person Place Metrics
- place: Instantaneous common place measurement of all customers, which may come from the change’s empirical values.
- pos: place measurement held by any person
- X: Sum of the traded quantity inside MMR ranges over the buying and selling interval
- MMRup: Higher restrict for MMR
- rMMR: Closing worth of the MMR
- R: precise distance from finest bid or ask, not the identical as r, typically depends upon i, j
Adjustment of MMR with Order Movement
The velocity of restrict order entries and cancellations is included as a part of the typical over a number of ranges. On condition that market orders usually tend to execute immediately, we have to account for this relative improve or lower. The next relationships outline the dynamics:
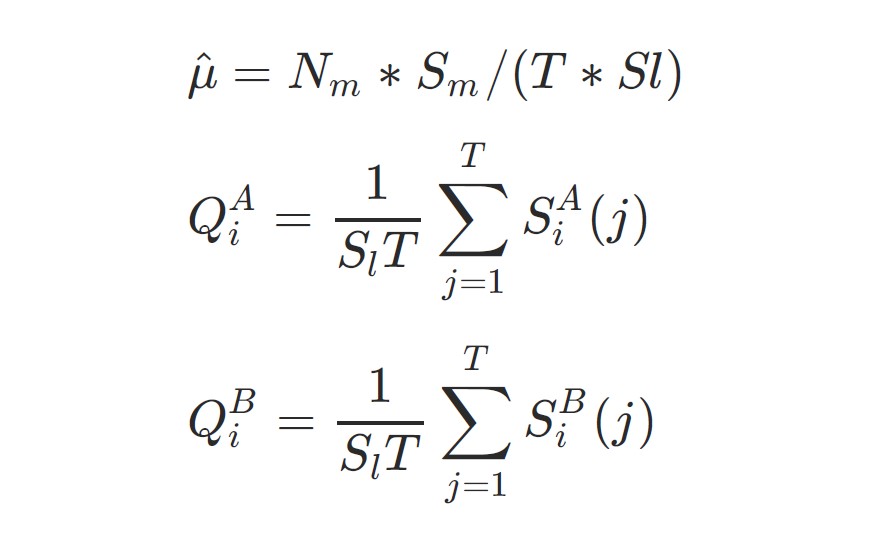
For instance, taking a protracted place, the corresponding robust liquidation liquidity might be the purchase order amount (Q):
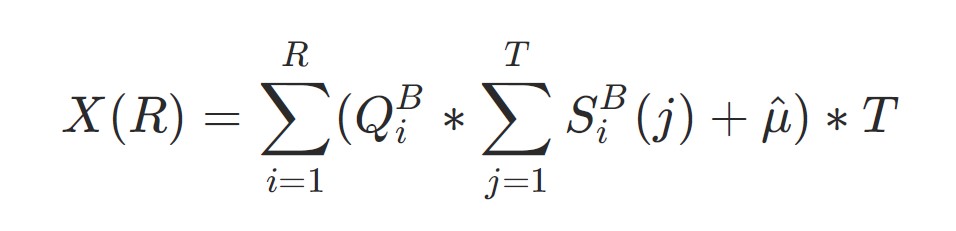
For change’s safety, we get:
X(R) = place R = f (place)
R = f (place)
Right here, it isn’t far to achieve that place and R have an roughly inverse relationship. And for minimal order amount:
R = p × MMR
The place is thought, given the constraint relationships of variables. MMR is impartial of p, so:
MMR = g(place) = z(Q, S, T , μ^, i, j) = f(place)/p
Subsequently, the ultimate worth of rMMR might be expressed as:
rMMR = min(MMRup, MMR)
From the above equations, it may be seen that, aside from R, different variables equivalent to place, Q, S and T are all decided. Thus, R might be derived from these variables, and subsequently, MMR and rMMR might be calculated.
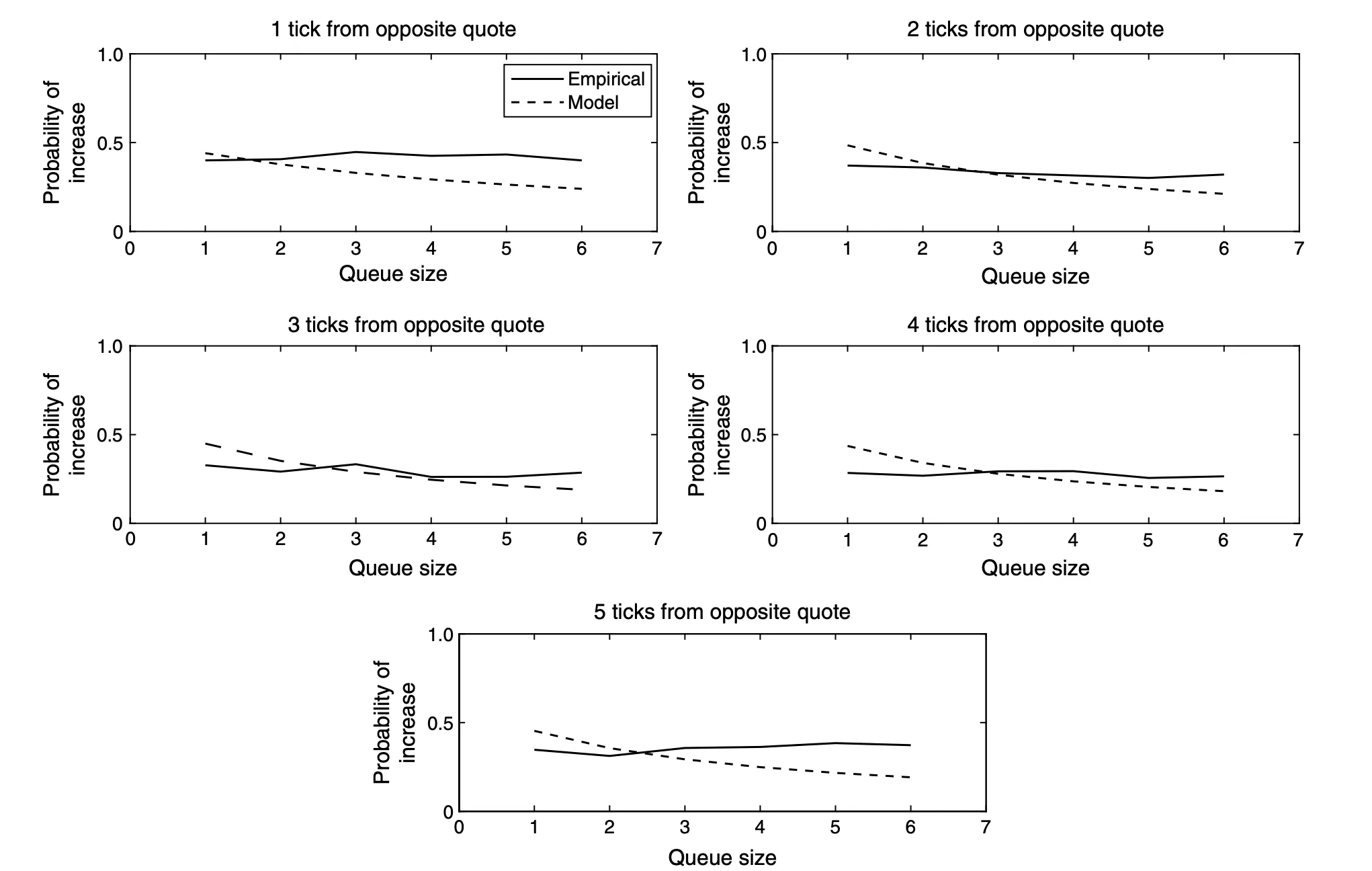
Moreover, the MMRup cap is important as a result of the mannequin tends to be conservatively estimated, typically ignoring the optimistic affect of key worth factors and key bid or ask ranges on the order e book. Some research from CME (see Determine 2) illustrate this impact extra precisely.
The IMR (Preliminary Margin Fee) is usually related to the leverage and liquidity of the underlying asset. Subsequently, it typically requires dynamic adjustment primarily based on elements equivalent to place measurement. It may be outlined as:
IMR = max(r, w(rMMR))
Right here, the IMR corresponds to the preliminary margin price r talked about in Part 2.1. The perform w(rMMR) presents extra flexibility. For instance, if the change considers its liquidity to be secure, it will probably apply a easy adjustment equivalent to: w(rMMR)=1.3×rMMR.
This method gives a practical approach to dynamically regulate margin charges, making certain that the IMR displays present market circumstances and liquidity ranges. This makes the system extra adaptive in comparison with fastened margin guidelines, benefiting each customers and the change by way of efficient threat administration.
An approximate resolution for ok
The parameter ok serves as a world setting for every particular asset (image) and doesn’t must account for present orders or open positions. In precept, the bigger the worth of ok, the extra positions a person can open. Nevertheless, there’s a important constraint: the margin required for the utmost allowable place should not exceed the whole capital multiplied by the IMR.
To simplify, let’s assign the utmost allowable place system to a variable v:
v = ok ∗ ln(C/(p ∗ r ∗ ok) + 1)
The precise leverage should be lower than or equal to the reciprocal of the utilized margin:
v/(C/p) <= 1/max(r, f (v, rMMR))
Let’s introduce a brand new variable y to switch C (capital) and p (worth) for simplification:
y = C/p
we get:
v <= y/max(r, f (v, rMMR))
Besides for terribly small positions, 1.3 × rMMR (a simplified adjustment utilizing f(pos,rMMR) is usually lower than r. For smaller positions, the margin required turns into negligible, so such eventualities will not be a priority for our threat mannequin. Equally, since MMRup units an higher restrict, it can be ignored on this context.
Thus, we solely want to contemplate the smallest attainable worth for 1/IMR. The inequality can due to this fact be simplified as:
v <= y/(1.3 ∗ f (place)/p)
This inequality demonstrates the connection between the utmost allowable place and precise leverage.
In contrast to different variables, place and R have a clearly outlined inverse relationship. Subsequently, the MMR derived from R also can have an inverse proportional relationship with place, and MMR might be expressed as follows:
MMR = para1 + para2/place
At this level, to imagine that the MMR beneath low positions aligns with the standard type (half of the inverse of leverage), the system might be written as:
MMR = 1/(2 ∗ maxleverage) ∗ (1 + pos/place)
Now we try to seek out the restrict of ok, then r in system (3) turns into 1/maxleverage.
And, substituting the variables, the inequality (18) can develop into:
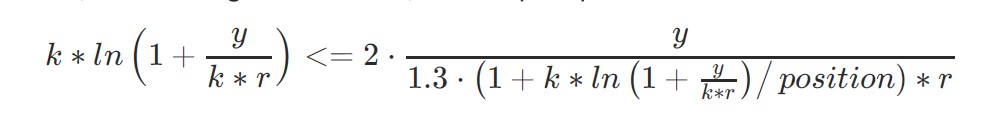
We observe that y (decided by the person’s capital) theoretically mustn’t have an effect on the worth of ok. Thus, ok is primarily depending on place. Though the minimal worth of ok varies with modifications in y, the target is to establish the smallest attainable minimal throughout all circumstances. This ensures that the opening of positions stays secure beneath any situation.
Right here, y/(ok*r) can nonetheless be substituted by a variable, however the equation stays complicated and tough to resolve analytically. Some in depth approximation experiments and iterative simulations reveal that ok converges to a quite simple expression(however the calculation of ok is a big enterprise, so it is not going to be elaborated on intimately right here):
ok <= e ∗ place
By adjusting the values of ok or place, we are able to obtain the impact that when the quantity of funds or the variety of open positions is just not giant, customers can divulge heart’s contents to C/(p∗r). In any other case, they are going to be restricted. The dimensions of the amount and the diploma of limitation are each managed by ok and place. Subsequently, totally different cryptocurrencies typically correspond to totally different ok values.
The above is a quick introduction to KuCoin’s cross-margin threat restrict system. Some great benefits of this design and its user-friendliness are self-evident.
In KuCoin’s cross-margin system, apart from threat limits, different components equivalent to threat ratios and order margin utilization are additionally dynamically managed utilizing the mark worth. This dynamic administration not solely maximizes the discharge of customers’ margin but additionally integrates seamlessly with the brand new threat restrict framework, enhancing system effectivity and person expertise.
determine 1:
determine 2:
- “A Stochastic Mannequin for Order Guide Dynamics” by Rama Cont, Sasha Stoikov, and Rishi Talreja, Operations Analysis, Quantity 58, Subject 3, in 2010.
- “Forecasting Preliminary Margin Necessities – A Mannequin Analysis” , Journal of Monetary Markets (Quantity 40, 2018)
- Alfonsi, A., A. Schied, A. Schulz. 2010. Optimum execution methods in restrict order books with normal form capabilities. Quant. Finance 10(2).
Disclaimer: The knowledge offered on this article is for informational and academic functions solely. The article doesn’t represent monetary recommendation or recommendation of any variety. Coin Version is just not chargeable for any losses incurred on account of the utilization of content material, merchandise, or providers talked about. Readers are suggested to train warning earlier than taking any motion associated to the corporate.

